Release time:Jun 04, 2025
At the 2025 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting held in Chicago, USA, from May 30 to June 3, the results of the Phase Ib/II clinical study of 9MW2821 in combination with toripalimab for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (la/mUc) were presented by Prof. Xinan Sheng, Chief Physician of the Department of Urologic Oncology, Beijing Cancer Hospital, on behalf of the research team, with key highlights as below:
Oral Presentation
Background:
Urothelial carcinoma (UC) is a common malignant tumor worldwide. Global cancer statistics released in 2024 showed that bladder cancer is the ninth most commonly diagnosed cancer in the world, with about 614,000 new cases and 220,000 deaths annually. The burden and morbidity of bladder cancer is significantly higher in men than in women. It is the sixth most common cancer and the ninth leading cause of cancer death in men [1].
9MW2821 (Bulumtatug Fuvedotin, BFv) is a next-generation Nectin-4 targeting antibody-drug conjugate. Previous study of BFv has shown promising efficacy in la/mUC patients who progressed on/after platinum-based chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors [2]. A pivotal phase 3 study of BFv is ongoing in China (NCT06196736, CTR20234024).
Toripalimab is a novel recombinant humanized anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody that has been approved in multiple countries including China and the USA.
It is the first time to report in detail on the efficacy and safety of 9MW2821 in combination with Toripalimab in patients with la/mUC.
Method:
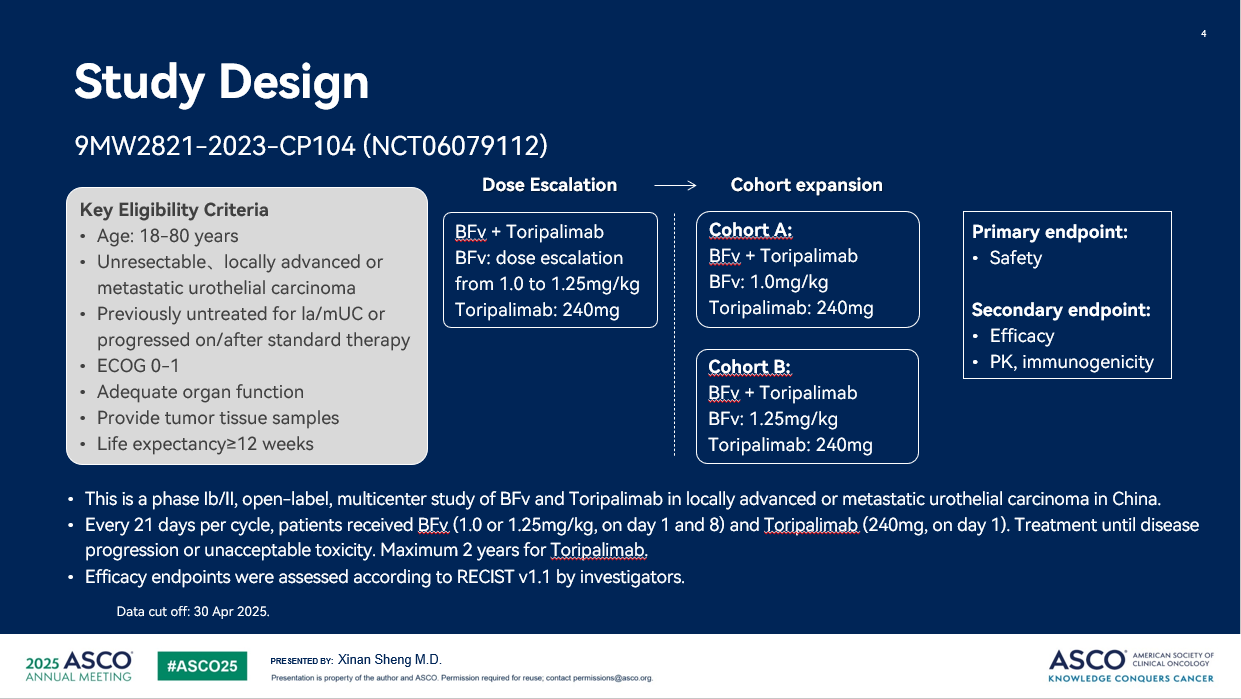
This is a phase Ib/II, open-label, multicenter study of BFv and Toripalimab in la/mUC in China. Every 21 days per cycle, patients received BFv (1.0 or 1.25mg/kg, on day 1 and 8) and Toripalimab (240mg, on day 1). Treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Results:
As of Apr. 30, 2025, 52 patients with la/mUC were enrolled. Among the 40 assessable patients (treatment-naive for la/mUC) with the median age of 67, 70% of patients were male, 72.5% had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) score of 1, 55% with tumor primary site at upper urinary tract, 15% had liver metastases, 82.5% were Nectin-4 positive and 20% were PD-L1 positive.
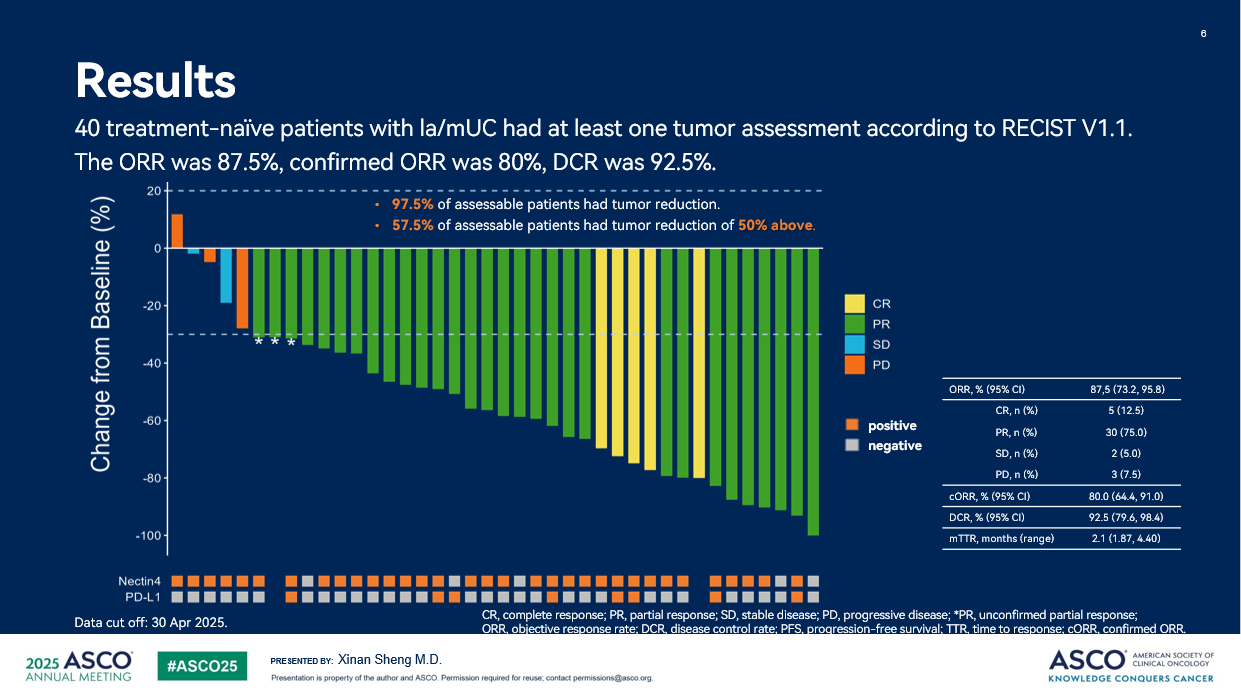
The Objective Response Rate (ORR) was 87.5% (95% CI: 73.2, 95.8), confirmed ORR was 80%, complete response (CR) rate was 12.5%, Disease Control Rate (DCR) was 92.5% (95% CI: 79.6, 98.4). 97.5% of assessable patients had tumor reduction, 57.5% of assessable patients had tumor reduction of 50% above.
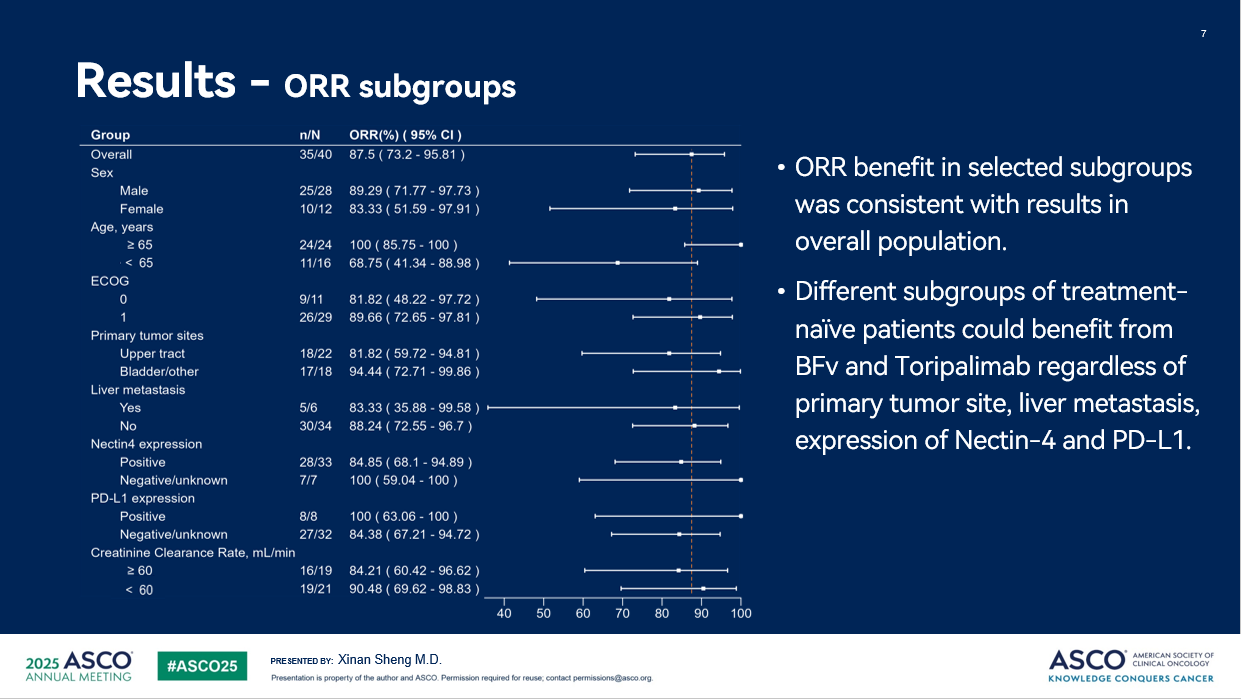
The ORR in selected subgroups was consistent with results in overall population. Different subgroups of treatment-naive patients could benefit from BFv and Toripalimab regardless of primary tumor site, liver metastasis, expression of Nectin-4 and PD-L1. The ORR was 100% (24/24) in patients older than 65, 94.44% (17/18) in patients with tumor primary site at lower urinary tract, 83.33% (5/6) in patients with liver metastasis, 100% (7/7) in nectin-4 negative patients, and 100% (8/8) in PD-L1 positive patients.
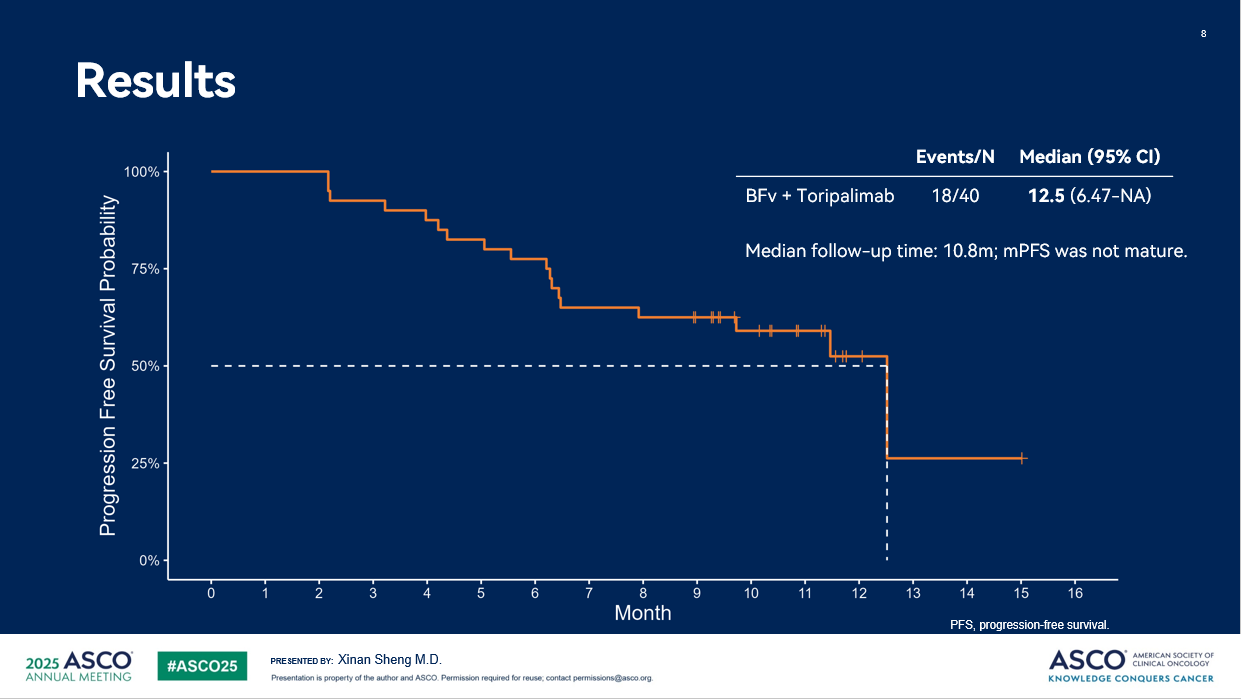
As of April 30, 2025, 45% (18/40) of subjects experienced disease progression or death, with a median progression-free survival (mPFS) of 12.5 months (95% CI: 6.47-NA), and a median duration of response (mDoR) that has not been reached. Median follow-up time was 10.8 months, thus mPFS and mDoR were not mature.
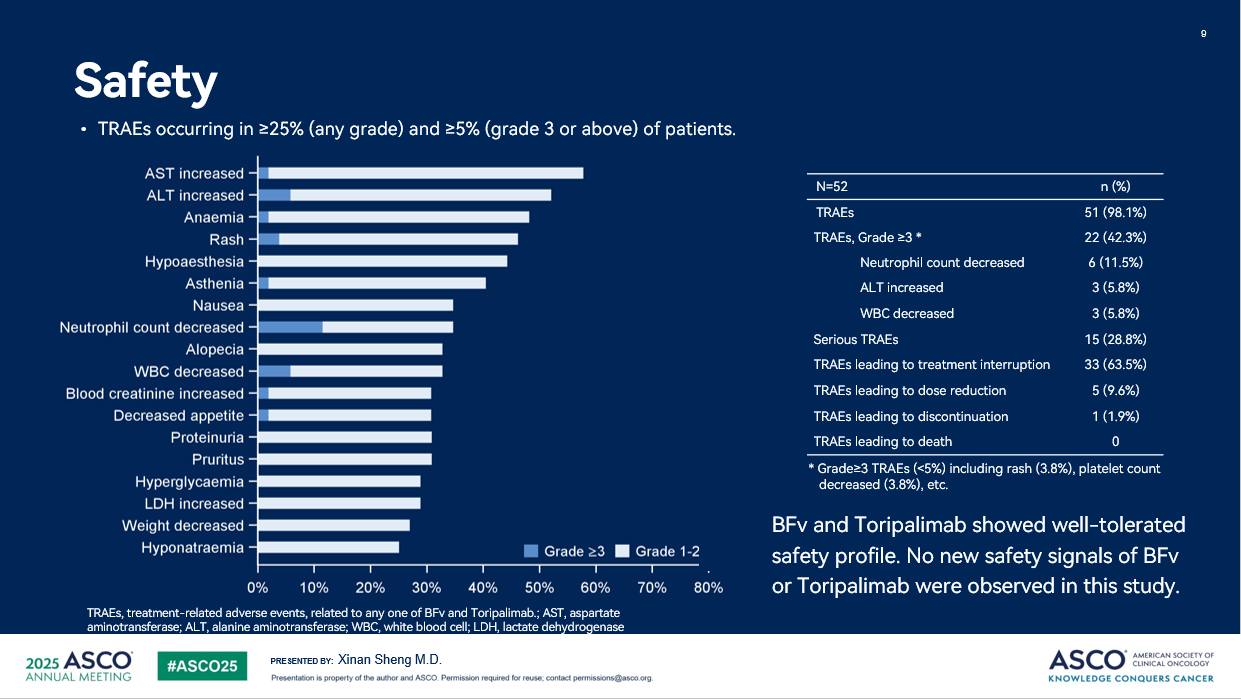
The incidence rate of treatment-related adverse events (TRAE) was 98.1%, and most of the TRAEs were grade 1-2. The incidence rate of TRAEs ≥grade 3 was 42.3%, mainly characterized by neutrophil counts decreased (11.5%), alanine aminotransferase increased (5.8%), and white blood cell decreased (5.8%). The incidence rate of serious TRAEs was 28.8%, and no TRAEs leading to death occurred. BFv and Toripalimab showed well-tolerated safety profile. No new safety signals of BFv or Toripalimab were observed in this study.
Conclusion:
BFv combined with Toripalimab has demonstrated encouraging efficacy and manageable safety profile in la/mUC. Patients with advanced age, liver metastases and negative expression of Nectin-4 also achieved considerable response in this study, suggesting that BFv in combination with Toripalimab may provide a new treatment option for patients with advanced UC who are intolerant of or potentially have a poor prognosis with platinum-based chemotherapy. A pivotal phase 3 study of BFv combined with Toripalimab vs platinum-based chemotherapy is ongoing in China (NCT06592326, CTR20242828).
About 9MW2821
9MW2821 is a novel Nectin-4 targeting ADC, which achieves site-specific modification of antibody through proprietary conjugate technology linkers and optimized ADC conjugation process of Mabwell. It stands out as the first clinical-stage drug candidate among Chinese companies for this specific target. And it’s the first Nectin-4 targeting ADC to disclose clinical efficacy data in cervical, esophageal, and breast cancers. 3 Phase III pivotal clinical trials are ongoing. Its monotherapy and combination therapy with Toripalimab for UC have been granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation (BTD) by the Center for Drug Evaluation (CDE) of the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in China. It has also been granted Fast Track Designations (FTD) for 3 indications and Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) for 1 indication by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
[1] Bray F, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024;
[2] Zhang et al. ASCO 2024.